VFP to Servoy Code Reference
The idea behind this page is to provide an extensive list of coding practises that are familiar in Visual FoxPro and show their counterpart in Servoy.
Of course, Visual FoxPro and Servoy are very different in a lot of areas but there are many similarities too. You should also realize that Visual FoxPro is much more a low-level programming language than Servoy where a lot of functionality is taken care of automatically.
So if a syntax counterpart is not present in Servoy that is not necessarily a bad thing.
Filling this page is a daunting task that will take forever and will never be complete. However, some of you have offered to assist in contributing to this site. Ideally, with your help, this page could be filled rapidly with lots of valuable content so please contribute!
Based on the information below we could build a library with functions that work exactly the same as in FoxPro (a VFP Toolkit for Servoy so to speak). But I believe it's better to learn the language as intended and keep your programs maintainable/exchangeable with other Servoy developers.
To get things started I've added a few functions and statements. Expect expansion on a regular basis.
Visual FoxPro
Servoy
application.getClipboardString()
plugins.file.getFolderContents()
string.toLowerCase().indexOf()
plugins.file.getHomeDirectory()
application.showColorChooser()
plugins.file.showDirectorySelectDialog()
plugins.file.showFileOpenDialog()
controller.setSelectedIndex(n);
controller.setSelectedIndex(1);
controller.setSelectedIndex(n);
plugins.file.getHomeDirectory()
plugins.dialogs.showInputDialog()
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog
plugins.dialog.showInfoDialog()
plugins.file.showFileSaveDialog()
controller.setSelectedIndex(controller.getSelectedIndex()+1);
plugins.file.appendToTXTFile()
application.getScreenHeight() | application.getScreenWidth()
$ - globals.CONTAINS()
Returns true if a character expression is contained in another character expression.
VFP code example
? "b" $ "abc"
? "World" $ "Hello World"
? "world" $ "Hello World"
&& returns .T.
&& returns .T.
&& returns .F.
Servoy code example
var cSearchFor = "World";
var cString = "Hello World";
if(cString.IndexOf>-1) {
return true; // returns true
}else{
return false;
}
// alternatively:
globals.CONTAINS("World","Hello World!");// returns true
= | ==
This may be confusing at first but in Visual Foxpro the = operator is used both for testing equality and as an assignment operator. In Servoy/Javascript the = operator is an assigment operator only! The == operator is used for testing equality and works the same as in VFP. In VFP you can partially compare strings (where "abcde" = "abc" but only if SET EXACT=OFF) which you cannot do in Javascript (using the = operator).
VFP code example
x = 20 && assigns 20 to variable x
? x=20 && returns .T.
name = "Smith" && assigns "Smith" to variable name
? name = "Smi" && returns .T. !!
? name == "Smi" && returns .F.
? name == "Smith " && returns .F. !!
? name == alltrim("Smith ") && returns .T.
Servoy code example
var cSearchFor = "World";
var cString = "Hello World";
if(cString.IndexOf>-1) {
return true; // returns true
}else{
return false;
}
// alternatively:
globals.CONTAINS("World","Hello World!");// returns true
^ | ** - Math.pow()
Returns base to the exponent power.
VFP code example
? 3 ^ 8 && Returns 6561
? 3 ** 8 && Returns 6561
Servoy code example
Math.pow(3,8); // returns 6561.0
// or alternatively:
globals.POWER(3, 8) // returns 6561.0
MOD() | % - %
Divides one numeric expression by another numeric expression and returns the remainder.
VFP code example
? 11 % 3 && returns 2
?MOD(11,3) && returns 2
Servoy code example
11 % 3; // returns 2
// alternatively:
globals.MOD(11,3); // returns 2
? - application.output()
Evaluates expressions and sends the results to output location (main screen in VFP or the Debug Console in Servoy).
VFP code example
? "Hello"
** shows Hello in the Visual FoxPro background screen (_Screen)
Servoy code example
application.output("Hello");
// shows Hello in the Debug Console
// if you don't see it press Alt+Shift+Q, C
_CLIPTEXT - application.getClipboardString() | application.setClipboardContent()
Get or set the contents of the Clipboard. If a string parameter is passed, the contents will be placed on the Clipboard. If no parameter is passed the current contents of the Clipboard will be returned. In VFP the Clipboard is accessible through a system variable. Since it is not possible to implent Get/Set on a variable in Servoy a _CLIPTEXT function is the next best thing.
VFP code example
cText =_CLIPTEXT&& gets the clipboard contents and puts them in a string
_CLIPTEXT= "Hello"&& places a string on the clipboard
Servoy code example
var cText=application.getClipboardString();// retrieves the clipboard
application.setClipboardContent("Hello"); // sets the clipboard
// alternatively:
var cText=globals._CLIPTEXT(); // retrieves the clipboard
globals._CLIPTEXT("Hello"); // sets the clipboard
Note: _CLIPTEXT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ABS() - Math.abs()
Returns the absolute value of the specified numeric expression.
VFP code example
nResult = (10-20)
? ABS(nResult)
** result: 10
Servoy code example
var nResult = (10-20);
Math.abs(nResult);
// result: 10.0
Note: ABS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ACOPY() - array.slice
Copies elements from one array to another array.
VFP code example
Copy complete array
DIMENSIONaArray(4)
aArray(1)="Jones"
aArray(2)="Smith"
aArray(3)="Peter"
aArray(4)="John"
DIMENSION aTest(4)&& The array needs to be declared before copying
ACOPY(aArray, aTest)&& copies array aArray to aTest
Copy array partially
DIMENSIONaTest(2)&& The array needs to be declared before copying
ACOPY(aArray, aTest, 2, 2)&& start copy at element 2 and copy 2
&& copies Smith and Peter
Servoy code example
Copy complete array
varaArray=["Jones", "Smith", "Peter", "John"];
varaTest=aArray// copies array aArray to aTest
Copy array partially
varaTest=aArray.slice(1,3)// start copy at element 1 and end at 3
aTest[0]// outputs Smith
aTest[1]// outputs Peter
aTest[2]// not there
ACOS() - Math.acos()
Returns in radians the arc cosine of a numeric expression.
VFP code example
?ACOS(0.5)&& 1.0471975511965980
Servoy code example
Math.acos(0.5)// 1.0471975511965979
ADDBS() - globals.ADDBS()
Adds a backslash (if needed) to a path expression.
VFP code example
*-- Both print C:\Windows\
?ADDBS( "C:\Windows" )
?ADDBS( "C:\Windows\" )
Servoy code example
// Both print C:\Windows\
globals.ADDBS("C:\Windows")
globals.ADDBS("C:\Windows\")
Note: ADDBS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ADIR() - plugins.file.getFolderContents
Returns an array with file/directory information. In VFP you have to specify the name of the array and don't have to specify a folder (the current directory is used). In Servoy you don't have to specify the name of the array but must specify the name of the folder. The ADIR() function therefor deviates from the VFP functionality and conforms to the Servoy way of doing it.
There are more differences. In VFP can you use wildcard characters such as * and ?. VFP fills a two-dimensional array with fileinfo. Servoy fills a one-dimensional array with JSFile objects which allow you to retrieve more fileinfo from the objects.
VFP code example
?ADIR(aTest, "c:\temp\")&& fills two-dim.array and returns filecount
?ADIR(aTest, "c:\temp\", "*.prg")&& just get the programs
?ADIR(aTest, "c:\temp\", "???_*", "D")&& just dirs starting with mask
? aTest(10,1)&& filename
? aTest(10,2)&& filesize
? aTest(10,3)&& date modified
? aTest(10,4)&& time modified
? aTest(10,5)&& attributes
Servoy code example
var dirArray =plugins.file.getFolderContents("c:\\temp\\");
var dirArray =plugins.file.getFolderContents("c:\\temp\\",".prg");
var dirArray =plugins.file.getFolderContents("c:\\temp\\", "",2);
dirArray[1].getName() // name of the file or directory
dirArray[1].size() // filesize
dirArray[1].lastModified() // filesize
dirArray[1].isHidden() // true if hidden
dirArray[1].getContentType()// ie application/zip, application/pdf etc.
// alternatively:
globals.ADIR("c:\\temp\\"); // array with jsfile objects
globals.ADIR("c:\\temp\\",".prg");// just programs
globals.ADIR("c:\\temp\\", "",2); // only directories
Note: ADIR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ALEN() - array.length
Returns the number of elements in the array. In Visual FoxPro the ALEN function can also return the number of rows or columns in a two-dimensional array.
VFP code example
DIMENSIONmyArray(2,3) && create an array of 2 rows and 3 columns
? ALEN(myArray)&& returns 6 (2*3 elements)
? ALEN(myArray,1)&& returns 2 (rows)
? ALEN(myArray,2)&& returns 3 (columns)
Servoy code example
varmyArray=newArray(2); // array with 2 elements
myArray = ['a', 'b']
application.output(myArray[0]) // returns a ZERO-BASED!
application.output(myArray[1]) // returns b
application.output(myArray.length)// returns 2
ALLTRIM() - utils.stringTrim()
Removes all leading and trailing spaces from the specified character expression.
VFP code example
myString = ALLTRIM(" Hello ")
Servoy code example
var myString = utils.stringTrim(" Hello ")
AND, OR, NOT - &&, ||, !
Logical operators work with all data types and return a Logical value.
VFP code example
IFnAmount > 10 AND nAmount <= 100// logical AND
IFnAmount <= 10 OR (nAmount > 10 AND nAmount <= 20)// logical OR
IFNOT nAmount = 10// logical NOT (! and .NOT. are also valid)
Servoy code example
if(nAmount>10&&nAmount<=100)// logical AND
if(nAmount=10||(nAmount>10&&nAmount<=20))// logical OR
if(nAmount!=10)// logical NOT
APRINTERS() - application.getPrinters()
Returns an array with printernames.
VFP code example
?APRINTERS(aTest, "c:\temp\")&& fills five-column array
? aTest(1,1)&& printername
? aTest(1,2)&& name of the printerport
? aTest(1,3)&& name of the printerdriver
? aTest(1,4)&& printer comment
? aTest(1,5)&& printer location
Servoy code example
// returns array with printer names
var prnArray =application.getPrinters();
// alternatively:
// returns array with printer names
globals.APRINTERS();
Note: APRINTERS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ASC() - string.charCodeAt()
Returns the ANSI value for the specified character in a character expression.
VFP code example
cString = "Hé"
?ASC(SUBSTR(cString,2,1))&& returns 233
Servoy code example
varcString="Hé";
application.output(cString.charCodeAt(1))// outputs 233
// Watch out for the fact that the charCodeAt() function expects a
// zero-based index position. To get the charCode for the first
// character in the string you would have to pass in a 0 as a
// parameter
Note: Alternatively use the ASC() function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ASCAN() - array.indexOf
Searches an array for an element containing the same data and data type as an expression.
VFP code example
DIMENSIONaArray(4)
aArray(1)="Jones"
aArray(2)="Smith"
aArray(3)="Peter"
aArray(4)="John"
?ASCAN(aArray, "Peter")&& returns 3
Servoy code example
varaArray=["Jones", "Smith", "Peter", "John"];
application.output(aArray.indexOf("Peter"))// outputs 2 (zero-based!)
ASIN() - Math.atan()
Returns in radians the arc sine of a numeric expression.
VFP code example
?ASIN(0.65)&& -0.7075844367253560
Servoy code example
Math.asin(-0.65)// -0.7075844367253556
ASORT() - array.sort
Sorts elements in an array.
VFP code example
DIMENSIONaWords(6)
aWords(1)= "limit"
aWords(2)= "lines"
aWords(3)= "finish"
aWords(4)= "complete"
aWords(5)= "In"
aWords(6)= "Out"
ASORT(aWords)
? aWords(1)&& returns In
? aWords(2)&& returns Out
? aWords(3)&& returns complete
? aWords(4)&& returns finish
? aWords(5)&& returns limit
? aWords(6)&& returns lines
Servoy code example
varwords=new Array("limit","lines","finish","complete","In","Out"); words.sort();
words[0];// returns Inn
words[1];// returns Outt
words[2];// returns completee
words[3];// returns finishh
words[4];// returns limitt
words[5];// returns linee
AT() - string.indexOf()
Searches a character expression for the occurrence of another character expression and returns the position where the string was found. In Servoy the position is zero-based, the first character is at position 0, for VFP this is position 1. If the searchString was not found then VFP returns a 0 and Servoy returns -1. This is important to remember.
VFP code example
?AT("World", "Hello World")&& returns 7
?AT("Hi", "Hello World")&& returns 0
Servoy code example
varcString="Hello World";
application.output(cString.indexOf("World"))// outputs 6 !!
application.output(cString.indexOf("Hi"))// outputs -1 !!
Note: AT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ATAN() - Math.atan()
Returns in radians the arc tangent of a numeric expression.
VFP code example
?ATAN(PI()/2)&& 1.003884821853887
Servoy code example
Math.atan(Math.PI/2)// 1.0038848218538872
ATC() - string.toLowerCase().indexOf()
Searches a character expression for the occurrence of another character expression and returns the position where the string was found, without regard for the case of these two expressions. In Servoy the position is zero-based, the first character is at position 0, for VFP this is position 1. If the searchString was not found then VFP returns a 0 and Servoy returns -1. This is important to remember.
Because Servoy/Javascript does not have a direct counterpart for ATC() (or I missed it), the same effect can be realised by using the code below. However, this requires the search expression to be entered in lower case.
VFP code example
?ATC("world", "Hello World")&& returns 7
?ATC("Hi", "Hello World")&& returns 0
Servoy code example
varcString="Hello World";
application.output(cString.toLowerCase().indexOf("world"))
// outputs 6 !!
application.output(cString.toLowerCase().indexOf("Hi"))
// outputs -1 !!
Note: ATC() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
BETWEEN() - globals.BETWEEN()
Determines whether the value of an expression is inclusively between the values of two expressions of the same type.
VFP code example
? BETWEEN("b", "a", "c") && Outputs .T.
? BETWEEN("a", "b", "c") && Outputs .F.
? BETWEEN("a", .NULL., "c") && Outputs .NULL.
? BETWEEN("3", "1", "5") && Outputs .T.
? BETWEEN(3, 1, 5) && Outputs .T.
? BETWEEN(2, 1, 2) && Outputs .T.
d1=DATE(2011,2,15)
d2=DATE(2011,1,1)
d3=DATE(2011,3,1)
? BETWEEN(d1, d2, d3) && Outputs .T.
Servoy code example
globals.BETWEEN("b","a","c");// true
globals.BETWEEN("a","b","c");// false
globals.BETWEEN("3","1","5");// true
globals.BETWEEN(3, 1, 5);// true
globals.BETWEEN(3,null, 5);// null
globals.BETWEEN(2, 1, 2); // true
vard1=new Date(2011,2,1);
vard2=new Date(2011,1,1);
vard3=new Date(2011,3,1);
globals.BETWEEN(d1, d2, d3);// true
Note: BETWEEN() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CANCEL - application.exit()
Ends execution of the current application. I don't think you would want to call globals.CANCEL() instead of application.exit() but as a code reference it serves its purpose.
VFP code example
CANCEL
Servoy code example
CDOW() - globals.CDOW()
Returns the day of the week from a given Date or DateTime expression.
VFP code example
d =DATE(2072,10,15)
?CDOW(d)// Saturday
Servoy code example
utils.stringFormat('%tA', new Array(new Date(2072,9,15)))// Saturday
// OR using the CDOW() function alternative:
vard=newDate(2072,9,15)// MONTH 9 = OCTOBER !!
application.output(globals.CDOW(d))// saturday/samstag/zaterdag
Note: CDOW() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CEILING() - Math.ceil()
Returns the next highest integer that is greater than or equal to the specified numeric expression.
VFP code example
amount = 2.33
?CEILING(amount)// Returns 3
Servoy code example
varamount=2.33;
globals.CEILING(amount); // returns 3.0
Note: CEILING() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CHR() - utils.getUnicodeCharacter()
Returns the Unicode character associated with the specified number. In VFP the Ansi code character is used and in Servoy the Unicode character is used. Of course the latter is preferable.
VFP code example
CHR(100) && returns d
Servoy code example
utils.getUnicodeCharacter(100); //return d
// alternatively:
globals.CHR(100);
Note: CHR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CHRTRAN() - globals.CHRTRAN()
Replaces each character in a character expression that matches a character in a second character expression with the corresponding character in a third character expression. This function does not exist in Servoy/Javascript. Therefor it has been custom coded in the VFP2Servoy toolkit.
VFP code example
?CHRTRAN('ABCDEF', 'ACE', 'XYZ')&& Displays XBYDZF
Servoy code example
globals.CHRTRAN('ABCDEF','ACE','XYZ');// Returns XBYDZF
Note: CHRTRAN() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CMONTH() - globals.CMONTH()
Returns the name of the month from a given date or DateTime expression.
VFP code example
d =DATE(2072,10,15)
?CMONTH(d)// October
Servoy code example
utils.stringFormat('%tB', new Array(new Date(2072,9,15)))
// OR using the CMONTH() function alternative:
vard=newDate(2072,9,15)// MONTH 9 = OCTOBER !!
application.output(globals.CMONTH(d))// October/oktober
Note: CMONTH() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
COPY FILE - plugins.file.copyFile()
The COPY FILE statement alternative in Servoy is implemented through thefileplugin with lots of file and directory functions in it. Note that VFP's SET SAFETY command determines if any existing file is overwritten, which is the default behaviour of the fileCopy() function in Servoy.
NOTE: You cannot specify a file path in Servoy with single backslashes in it. The backslash is used to specify special characters (\t=tab for instance). You will have to remember to always use TWO backslashes instead of one to specify a single backslash (c:\\temp\\ instead of c:\temp\). We can't solve this in the function because "c:\temp" will arive in the parameter as "c: temp" (with a tab in it).
You cannot use wildcard characters in filenames in Servoy.
VFP code example
COPY FILEc:\temp\test.xmlTOc:\temp\test.bak&& copies the file
COPY FILEc:\temp\*.xmlTOc:\temp\*.bak&& copies all xml files
Servoy code example
plugins.file.copyFile("c:\\temp\\test.xml","c:\\temp\\test.bak);
// alternatively:
globals.COPYFILE("c:\\temp\\test.xml","c:\\temp\\test.bak);
Note: COPYFILE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CTOD() - globals.CTOD()
Converts a character expression to a date expression.
VFP code example
?CTOD("13-01-2011")&& returns: 13-1-2011 as date
Servoy code example
globals.CTOD("01/13/2011"); // returns: 01/13/2011 as datetime
globals.CTOD("13-01-2011"); // returns: 01/13/2011 as datetime
Note: CTOD() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
CURDIR() - plugins.file.getHomeDirectory()
Returns the current directory.
VFP code example
?CURDIR()&& returns:\PROGRAM FILES (X86)\MICROSOFT VISUAL FOXPRO 9\
?FULLPATH(CURDIR())&& returns:"C:\PROGRAM FILES..."
Servoy code example
plugins.file.getHomeDirectory();// returns: C:\Users\<Computername>
//alternatively:
globals.CURDIR();// returns: C:\Users\<Computername>
Note: CURDIR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
DATE() - new Date()
Returns the current system date, which is controlled by the operating system, or creates a Date value. You will have a tough time trying to find the Servoy equivalent for VFP's Date(). It works just a little different.
VFP code example
?DATE()&& returns date (2/18/2011) in format of regional settings
d =DATE(2012,10,15)&& new date = 10/15/2012 (OCTOBER!)
Servoy code example
vard=newDate();
application.output(d);// Fri Feb 18 11:13:40 CET 2011
application.output(d.toLocaleDateString());// February 18, 2011
application.output(d.toDateString()); // Fri Feb 18 2011
utils.dateFormat(d,'d-M-yyyy'); // dutch date: 18-2-2011
// initialize a date value
vard=newDate(2012,9,15);// initialize a date valueOCTOBER=9
// vfp2servoy toolkit
vard=globals.DATE(2012,10,15)// initialize a date valueOCTOBER=10
NOTE: Alternatively use globals.DATE() of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
DATETIME() - new Date()
Returns the current system date, which is controlled by the operating system, or creates a Date value. You will have a tough time trying to find the Servoy equivalent for VFP's Date(). It works just a little different.
VFP code example
?DATETIME()&& returns (2/18/2011 12:54:28 PM) in regional format
Servoy code example
vard=newDate();
application.output(d);// Fri Feb 18 11:13:40 CET 2011application.output(d.toLocaleDateString());// February 18, 2011
application.output(d.toDateString());// Fri Feb 18 2011
application.output(d.toLocaleString()); // February 18, 2011 11:13:40 AM CET
application.output(d.toLocaleTimeString());// 11:13:40 AM CET
application.output(d.toLocaleString()); // Fri Feb 18 2011 11:13:40 GMT+0100 (CET)
application.output(d.toTimeString()); // 11:13:40 GMT+0100 (CET)
application.output(d.toUTCString()); //Fri, 18 Feb 2011 10:13:40 GMT
// dutch VFP datetime: 18-2-2011 20:13:40
utils.dateFormat(d,'d-M-yyyy HH:mm:ss')
DAY() - date.getDate()
Returns the numeric day of the month for a given date(time) expression.
VFP code example
d =DATE(2012,10,23)
? DAY(d) // 23
Servoy code example
vard=newDate(2012,9,23)// MONTH 9 = OCTOBER !!
application.output(d.getDate())// 23
// OR using the DAY() function alternative:
vard=newDate(2012,9,23)
application.output(globals.DAY(d))// 23
Note: DAY() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
DELETE FILE - plugins.file.deleteFile()
Erases a file from disk.
Servoy code example
plugins.file.deleteFile("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
// alternatively:
globals.DELETE_FILE("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
globals.ERASE("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
Note: DELETE_FILE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
Dimension - new Array()
Creates an array of variables.
VFP code example
Array with two elements
DIMENSIONmyArray(2)
myArray(1) = "a"
myArray(2) = "b"
Two dimensional array (2 rows, three columns)
DIMENSION myArray(2,3)
myArray(1,1) = "a"
myArray(1,2) = .T.
myArray(1,3) = "c"
myArray(2,1) = 18
myArray(2,2) = "hello"
myArray(2,3) =DATE()
Object array
DIMENSION MyArray[5]FOR x = 1 TO 5 MyArray[x] = CREATEOBJECT("CommandButton")ENDFOR
WATCH OUT! Arrays are zero-based in Servoy! See the samples.
Servoy code example
Empty array
varmyArray=newArray();
Short array declaration for two elements
varmyArray=['a', 'b'];
Array with a specified number of elements
varmyArray=new Array(2);
myArray[0] = 'a';//normal braces () don't work!
myArray[1] = 'b';//elements are zero-based
Shorter version of the same array
varmyArray=new Array('a', 'b');
Two-dimensional array
Sorry, no can do (or I didn't find out how)
Named array elements
varmyCustomer=new Array();
myCustomer['firstname']="John";
myCustomer['lastname']="Smith";
DIRECTORY() - plugins.File
Determines if the specified directory exists. Also the nFlags parameter can be used to differentiate in behaviour between normal directories and hidden directories.
VFP code example
?DIRECTORY("c:\temp\")&& .T. if the directory exists and is not hidden
?DIRECTORY("c:\temp\",0)&& .T. if the directory exists and is not hidden
?DIRECTORY("c:\temp\",1)&& .F. if the directory exists and is hidden
Servoy code example
var fs =plugins.file.convertToJSFile("c:\\temp\\");
// true if file exists
fs.exists();
// true if file is hidden
fs.isHidden();
// alternatively:
globals.DIRECTORY("c:\\temp\\"); // true if exists and not hidden
globals.DIRECTORY("c:\\temp\\",0);// true if exists and not hidden
globals.DIRECTORY("c:\\temp\\",1);// false if exists and is hidden
Note: DIRECTORY() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
Code Reference - DO CASE...ENDCASE / switch
The switch statement is one of the flow control programming constructs I am not so happy with. The DO CASE..ENDCASE is simpler and easier to use. But that's not all:
WATCH OUT! The main difference between theDO CASE...ENDCASEand theswitchis that theDO CASE...ENDCASEonly executes the first match. The switch executesallbranches below the first match unless abreak;is included, EVEN IF THEY DON'T MATCH!? BRR. By the way, this is not Servoy's fault, various other programming languages handle this the same.
VFP code example
Syntax:
DO CASE
CASE lExpression1
[Commands]
[CASE lExpression2
[Commands]]
...
[CASE lExpressionN
[Commands]]
[OTHERWISE
[Commands]]
ENDCASE
Sample
LOCAL lnChoice as Integer
lnChoice = MESSAGEBOX("Press a button",2)
DO CASE
CASE lnChoice = 3
MESSAGEBOX('You pressed the "Abort" button')
CASE lnChoice = 4
MESSAGEBOX('You pressed the "Retry" button')
CASE lnChoice = 5
MESSAGEBOX('You pressed the "Ignore" button')
OTHERWISE
MESSAGEBOX('No button was pressed')
ENDCASE
Servoy code example
Syntax:
switch( ### )
{
case:
default:
}
Sample
var choice = plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('Make a choice','Press a button','Yes', 'No', 'Maybe');
switch(choice) {
case 'Yes': {
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('Answer','You pressed the "Yes" button');
break;
}
case 'No': {
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('Answer','You pressed the "No" button');
break;
}
case 'Maybe': {
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('Answer','You pressed the "Maybe" button');
break;
}
default: {
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('Answer','You did not press a button');
break;
}
}
DO FORM - application.createNewFormInstance()
Create a new form instance. STOP! Before you run off to start initializing forms you should know that you usually don't have to create a new form instance. By default all forms are initialized and available through the Windows menu when the application is started.
So how do we activate a form then if it is allready initialized? Useapplication.ShowForm()instead. See the code below for an example.
VFP code example
DO FORMfrmTest
Servoy code example
// activate a form that has been initialized at application startup
// which is the default behaviour for all forms
application.showForm(forms.frmTest);
// If you want to instantiate an extra instance of a form then use
// application.createNewFormInstance()
application.createNewFormInstance("frmTest","ofrmTest2");
// How about a modal dialog popup style form? Also check out the other
// JSWindow types
varwin =application.createWindow("frmCustomers", JSWindow.MODAL_DIALOG); win.show("frmCustomers");
// And in the dialog close the form with the code or use the close box
controller.getWindow().destroy();
Note: DO_FORM() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit but using Native Servoy code as above is recommended.
DO WHILE...ENDDO - while
Executes a set of commands within a conditional loop. There are a few differences that should be noted. First notice the LOOP command in VFP that allows the flow to be reset to the beginning of the loop. Second notice that Javascript differentiates between ado whileloop and awhileloop. In thedo whileloop the action statement is carried out at least once, even if the test expression is false. In thewhileloop the action statement is only executed if the test expression is true.
VFP code example
counter = 0
max=10
DO WHILEcounter <= max
counter = counter + 1
? "Counter: " + counter
ENDDO
counter = 0
max = 10
DO WHILE.T.
counter = counter + 1
IFage > 65
LOOP
ENDIF
IFcounter >= max
EXIT
ENDIF
? "Hello" + name
ENDDO
Servoy code example
// output: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
varcounter = 0;
varmax = 10;
while(counter <= max)
{
counter += 1;
application.output(i);
}
// output: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
counter = 0;
do
{
counter += 1;
application.output(i);
if(lStop){
break;
}
}
while(counter <= max)
DTOC() - globals.DTOC()
Returns a date-string from a Date expression. DTOC is short forDate-To-Character.
VFP code example
?DTOC(DATE())// "4/15/2011" or "15-4-2011" depending on locale
?DTOC(DATE(),1)// "20110415" suitable for indexing
INDEX ON DTOC(dInvDate, 1)TAGdateIndex
Servoy code example
// March 4, 2011 / vrijdag 4 maart 2011 (depending on locale)
vard=newDate();
application.output(d.toLocaleDateString);
globals.DTOC(newDate())// "4/15/2011" or "15-4-2011" (localized)
globals.DTOC(newDate(),1)// "20110415" suitable for indexing
Note: DTOC() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
DTOS() - globals.DTOS()
Returns a character-string date in a yyyymmdd format from a specified date(time) expression.
VFP code example
DTOS(DATE())// "20110415" suitable for indexing
INDEX ON DTOS(dInvDate)TAGdateIndex
Servoy code example
vard=newDate();
utils.dateFormat(d,'yyyyMMdd')
// or alternatively:
vard=newDate();
globals.DTOS(d)// "20110415" suitable for indexing
Note: DTOS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
EMPTY() - globals.EMPTY()
Determines whether an expression evaluates to empty.
VFP code example
name = "Smith"
?EMPTY(name) // Returns .F.
?EMPTY(" ")// Returns .T.
number = 0
?EMPTY(number)// Returns .T.
date =DATE()
?EMPTY(date) // Returns .F.
bool = .T.
?EMPTY(bool) // Returns .F.
Servoy code example
varname="Smith";
globals.EMPTY(name); // returns false
globals.EMPTY(" "); // returns true
varnumber=0;
globals.EMPTY(number); // returns true
vardate=new Date();
globals.EMPTY(date); // returns false
varbool=true;
globals.EMPTY(bool); // returns false
Note: EMPTY() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ERASE - plugins.file.deleteFile()
Deletes a file from disk.
Servoy code example
plugins.file.deleteFile("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
// alternatively:
globals.ERASE("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
globals.DELETE_FILE("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
Note: ERASE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
EVALUATE() - eval()
Evaluates a character expression and returns the result.
Note! Be careful eval() might produce unexpected results! Also, combined with user input, eval() potentially forms a security risk. When evaluating variables inside a function they might be out of scope. Servoy says: eval()==evil. Use with caution.
VFP code example
cText = "ABS(-3.45)"
nResult =EVALUATE(cText)
? nResult && returns 3.45
Servoy code example
varcText ="Math.abs(-3.45)";
varnResult = eval(cText);
application.output(nResult); // returns 3.45
// alternatively:
globals.EVALUATE("Math.abs(-3.45)");// returns 3.45
Note: EVALUATE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
EXIT - break
Break allows you to exit a current loop, switch or label.
VFP code example
FORi = 1TO10
IFi = 7
? "Max. counter reached"
EXIT
ENDIF
NEXT
Servoy code example
for(vari=0; i<10; i++)
{
if(i==7){
application.output("Max. counter reached");
break;
}
}
EXP() - Math.exp()
Returns the value of ex where x is a specified numeric expression. The value of e, the base of natural logarithms, is approximately 2.71828
VFP code example
?EXP(2) && returns 7.38905609893065
Servoy code example
Math.exp(2);// returns 7.38905609893065
// alternatively:
globals.EXP(2); // returns 7.38905609893065
Note: EXP() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
FILE() | plugins.File
Determines if the specified file exists. Also the nFlags parameter can be used to differentiate in behaviour between normal files and hidden files.
VFP code example
?FILE("c:\temp\test.xml")&& .T. if the file exists and is not hidden
?FILE("c:\temp\test.xml",0)&& .T. if the file exists and is not hidden
?FILE("c:\temp\test.xml",1)&& .F. if the file exists and is hidden
Servoy code example
var fs =plugins.file.convertToJSFile("c:\\temp\\test.xml");
// true if file exists
fs.exists();
// true if file is hidden
fs.isHidden();
// alternatively:
globals.FILE("c:\\temp\\test.xml"); // true if exists and not hidden
globals.FILE("c:\\temp\\test.xml",0);// true if exists and not hidden
globals.FILE("c:\\temp\\test.xml",1);// false if exists and is hidden
Note: FILE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
FILETOSTR() - plugins.file.readTXTFile()
Returns the contents of a file as a character string.
VFP code example
cText =FILETOSTR("c:\temp\hello.txt")&& appends string
Servoy code example
var cText= plugins.file.readTXTFile("c:\\temp\\hello.txt");
// alternatively:
var cText=globals.FILETOSTR("c:\\temp\\hello.txt");
Note: FILETOSTR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
FLOOR() - Math.floor()
Returns the nearest integer that is less than or equal to the specified numeric expression.
VFP code example
amount = 2.33
?FLOOR(amount)// Returns 2
Servoy code example
varamount=2.33;
globals.FLOOR(amount); // returns 2.0
Note: FLOOR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
FOR...NEXT - for
Executes a set of commands within a conditional loop.
VFP code example
FORi = 1TO3
? "Counter value: " +TRANSFORM(i)
NEXT
Servoy code example
for(vari=0; i<3; i++)
{
application.output("Counter value: "+ i);
}
FOR EACH ... ENDFOR - array.ForEach()
Executes a set of commands for each element in an array.
VFP code example
DimensionmyArray(3)
myArray(1)="a"
myArray(2)="b"
myArray(3)="c"
For EachmyVarinmyArray
? myVar
EndFor
Servoy code example
functionprintAll(params) {application.output(params);}
vara=['a', 'b', 'c'];
a.forEach(printAll);
GETCOLOR() - application.showColorChooser()
Shows the Color Chooser Dialog. In VFP a default colornumber can be passed. In servoy a default colorstring can be passed. However most of the time you will call this function without any parameters, the point is to let the user choose a color.
VFP code example
?GETCOLOR() && returns a color number such as 255
Servoy code example
application.showColorChooser();// returns a color string such as #ff0000
// alternatively:
globals.GETCOLOR();
Note: GETCOLOR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GETDIR() - plugins.file.showDirectorySelectDialog()
Displays the Directory Select Dialog from which you can choose a directory.
Note: The GETDIR() function returns JSFile objects from which you can retrieve all the file/folder properties and file/folder manipulation methods. This is more powerful than just returning a string with the foldername and path.
VFP code example
cFolder =GETDIR()&& select a directory
Servoy code example
// returns JSFile (see plugins.file.JSFile for list of props & functions)
varcFolder= plugins.file.showDirectorySelectDialog();
cFolder.getPath();// c:\temp
cFolder.list();// [File1.txt, File2.txt]
cFolder.listFiles();// [C:\Temp\File1.txt, C:\Temp\File2.txt]
// alternatively:
// returns JSFile
var cFolder=globals.GETDIR();
cFolder.getPath();// c:\temp
cFolder.list();// [File1.txt, File2.txt]
cFolder.listFiles();// [C:\Temp\File1.txt, C:\Temp\File2.txt]
Note: GETDIR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GETFILE() - plugins.file.showFileOpenDialog()
Displays the Open File dialog box. The implementation in VFP is slightly different from the implementation in Servoy. The GETFILE() function in the VFP2Servoy Toolkit combines a bit of both. A nice addition for example is the ability to multiselect files.
Note: The GETFILE() function returns JSFile objects from which you can retrieve all the file properties and file manipulation methods. This is more powerful than just returning a string with the filename and path.
VFP code example
cFile =GETFILE(".txt")&& select a file
Servoy code example
// returns JSFile (see plugins.file.JSFile for list of props & functions)
varcFile=plugins.file.showFileOpenDialog(1,"c:\\temp\\",false,".txt");
cFile.getPath();
cFile.size();
cFile.lastModified();
// returns selected files as an array of JSFile objects
varaFiles= plugins.file.showFileOpenDialog(1,"c:\\temp\\",true,
[".txt",".pdf"],"c:\\temp\\",true,"","Select one or more files");
aFiles[1].getPath();
aFiles[1].size();
// alternatively:
// returns JSFile (see plugins.file.JSFile for list of props & functions)
varcFile=globals.GETFILE(".txt","c:\\temp\\");
cFile.getPath();
// returns selected files as an array of JSFile objects
varaFiles=globals.GETFILE([".txt",".pdf"],"c:\\temp\\",true,"",
"select one or more files");
aFiles[1].getPath();
Note: GETFILE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GETFONT() - application.showFontChooser()
Shows the Font Chooser Dialog.
VFP code example
?GETFONT() && returns the chosen font i.e.: Arial,12,B
Servoy code example
// 0=Regular, 1=Bold, 2=Italic, 3=BoldItalic
application.showFontChooser();// returns a font i.e.: Book Antiqua,0,11
// alternatively:
globals.GETFONT();
Note: GETFONT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GETWORDCOUNT() - utils.stringWordCount()
Counts the words in a string. The VFP2Servoy implementation als supports a delimiter parameter (see sample).
VFP code example
cString = "AAA aaa, BBB bbb, CCC ccc"
?GETWORDCOUNT(cString)&& Displays 6
Servoy code example
cString ="AAA aaa, BBB bbb, CCC ccc";
utils.stringWordCount(cString);// returns 6
// alternatively
cString ="AAA aaa, BBB bbb, CCC ccc";
globals.GETWORDCOUNT(cString); // returns 6
globals.GETWORDCOUNT(cString,",");// returns 3
Note: GETWORDCOUNT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GETWORDNUM() - utils.stringMiddleWords()
Returns a specified word from a string.
VFP code example
cString = "AAA aaa, BBB bbb, CCC ccc"
?GETWORDNUM(cString, 3)&& Displays BBB
?GETWORDNUM(cString, 3, ",") && Displays CCC ccc
Servoy code example
cString ="AAA aaa, BBB bbb, CCC ccc";
utils.stringMiddleWords(cString, 3, 1);// returns BBB
// alternatively
cString ="AAA aaa, BBB bbb, CCC ccc";
globals.GETWORDNUM(cString, 3); // returns BBB
globals.GETWORDNUM(cString, 3,",");// returns CCC ccc
Note: GETWORDNUM() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GO BOTTOM - controller.setSelectedIndex(foundset.getSize());
Makes the last record of the foundset the active record.
VFP code example
// go to the last record of the table
USECustomers
GO BOTTOM
// go to the last record of the remote view
USEv_customers// assumes you have created a remote view
GO BOTTOM
Servoy code example
// go to the last record of the foundset
controller.setSelectedIndex(foundset.getSize());
// Load all records and go to the last record (not wise with large tables)
var_nRecCount =databaseManager.getFoundSetCount(foundset);
var_oRecord = foundset.getRecord(_nRecCount);
controller.setSelectedIndex(_nRecCount);
// Sophisticated way of retrieving the last 200 results for tables larger // than lets say 5000 records where you dont want to load all data
foundset.clear();
if(_nRecCount>5000){
varargs =newArray();
args[0] = _nRecCount-200;
controller.loadRecords("select customer_id from customers where "+
"customer_id in (select customer_id from (select ROW_NUMBER() OVER "+
"(ORDER BY customers.customer_id) AS RowNumber, "+
"customers.customer_id from customers) as temp where "+
"temp.RowNumber>? order by RowNumber)", args);
controller.setSelectedIndex(200);
}
Note: GOBOTTOM() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GO TOP - controller.setSelectedIndex(1);
Makes the first record of the foundset the active record (selected record).
VFP code example
// go to the first record
USECustomers
GO TOP
Servoy code example
controller.setSelectedIndex(1);
Note: GOTOP() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
GOMONTH() - date.setMonth()
Returns the date that is a specified number of months before or after a given Datetime expression.
VFP code example
d =GOMONTH(DATE(),-3)&& Go 3 months back in time
Servoy code example
vard=newDate(dDate.setMonth(dDate.getMonth()+nMonths));
Note: Alternatively use the GOMONTH() function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
HOME() - plugins.file.getHomeDirectory()
Returns the home directory of the user that is currently logged in. IN VFP the HOME() function supports a parameter that allows you to differentiate between various Visual FoxPro directories. In Servoy only the users home directory is supported.
VFP code example
// returnsC:\Users\Computername\Documents\VisualFoxPro Projects
?HOME(8)
Servoy code example
plugins.file.getHomeDirectory();\\ returns C:\Users\Computername\
Note: HOME() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
DAY() - date.getHours()
Returns the hour portion from a DateTime expression.
VFP code example
?HOUR(DATETIME())// Returns a value between 0 and 23
Servoy code example
vard=newDate()
application.output(d.getHours()) // Returns a value between 0 and 23
// OR using the HOUR() function alternative:
vard=newDate()
application.output(globals.HOUR(d)) // Returns a value between 0 and 23
Note: HOUR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
Code Reference - if-else
Theifstatement is probably one of the very first statements you will be looking for since it's so commonly used in any programming language.
VFP code example
Syntax:
IF lExpression [THEN]
Commands
[ELSE
Commands]
ENDIF
Sample 1
IF var < 5
var = var + 1
ENDIF
Sample 2
IF var < 5
var = var + 1
ELSE
var = var - 1
ENDIF
Servoy code example
Syntax:
if (lExpression)
{
Commands;
}
[else
{
Commands;
}]
Sample 1
if (var < 5)
{
var = var + 1;
}
Sample 2
if (var < 5)
{
var = var + 1;
}
else
{
var = var - 1;
}
Sample 3
if (x < y)
return -1;
else if (x == y)
return 0;
else
return 1;
ID() - globals.ID()
returns network machine information when using Visual FoxPro in a network environment. The same functionality is available by using SYS(0).
VFP code example
?ID() // returns machine id and user id
Servoy code example
application.getHostName() + " # "+security.getSystemUserName()
Note: ID() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
IIF() - if..else
Returns one of two values depending on the value of a logical expression. Although Javascript does not have an immediate if statement it is possible to achieve the same effect by writing an if..else on one line.
VFP code example
?IIF(i = 7, "Value of i is 7", "Value of i is NOT 7")
Servoy code example
if(i==7){cString="Value of i is 7"}else{cString="Value of i is NOT 7"}
application.output(cString)
// alternatively:
varcString=globals.IIF(i==7,"Value of i is 7","Value of i is NOT 7");
Note: IIF() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
INLIST() - globals.INLIST()
Determines whether an expression matches another expression in a set of expressions.
VFP code example
cMonth =MONTH(customers.birthdate)
?INLIST(cMonth, 'January', 'February', 'March')
Servoy code example
var dDate = new Date();
var cMonth =utils.stringFormat('%tB', new Array(dDate));
globals.INLIST(cMonth,'January','February','March');
Note: INLIST() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
INT - globals.INT()
Evaluates a numeric expression and returns the integer portion of the expression. Because the Math library in Javascript does not have an INT() function it has been added to the VFP2Servoy Toolkit using serveral other Math functions.
VFP code example
INT(3.75)&& return 3
INT(-3.75)&& return 3
Servoy code example
varnum = -3.75
if(num < 0){Math.ceil(num)}else{Math.floor(num)};
// alternatively:
globals.INT(-3.75);
Note: INT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ISALPHA() - globals.ISALPHA()
ISALPHA() returns true if the leftmost character in the specified character expression is an alphabetic character; otherwise ISALPHA() returns false.
VFP code example
?ISALPHA('Abc')&& returns .T.
?ISALPHA('Äbc')&& returns .T.
?ISALPHA('9') && returns .F.
?ISALPHA('9ab') && returns .F.
?ISALPHA('éb89')&& returns .T.
?ISALPHA('_bcdef')&& returns .F.
Servoy code example
cString = "Äbc";
cString.charAt(0).match(/[^W0-9_]/)!=null;
// alternatively
globals.ISALPHA("Äbc");// Returns true
Note: ISALPHA() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ISDIGIT() - globals.ISDIGIT()
ISDIGIT() returns true if the leftmost character in the specified character expression is an alphabetic character; otherwise ISDIGIT() returns false.
VFP code example
?ISDIGIT('Abc')&& returns .F.
?ISDIGIT('Äbc')&& returns .F.
?ISDIGIT('9') && returns .T.
?ISDIGIT('9ab') && returns .T.
?ISDIGIT('Ab89')&& returns .F.
?ISDIGIT('_bcdef')&& returns .F.
Servoy code example
cString = "9ab";
cString.charAt(0).match(/[^W0-9_]/)!=null;
// alternatively
globals.ISDIGIT("9ab");// Returns true
Note: ISDIGIT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ISLOWER() - globals.ISLOWER()
Determines whether the leftmost character of the specified character expression is a lowercase alphabetic character.
VFP code example
?ISLOWER('Abc')&& returns .F.
?ISLOWER('abc')&& returns .T.
?ISLOWER('9ab') && returns .F.
?ISLOWER('éb89')&& returns .T.
?ISLOWER('_bcdef')&& returns .F.
Servoy code example
cString = "ábc";
cString.charAt(0).match(/[^W0-9_]/)!=null&&
cFirstCharacter == cFirstCharacter.toLowerCase();// returns true
// alternatively
globals.ISLOWER("Abc");// Returns false
globals.ISLOWER("abc"); // Returns true
globals.ISLOWER("9ab"); // Returns false
globals.ISLOWER("éb89"); // Returns true
globals.ISLOWER("_bcdef");// Returns false
Note: ISLOWER() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
EMPTY() - ==null
Returns true if an expression evaluates to a null value; otherwise, ISNULL() returns false.
VFP code example
name = .NULL.
?ISNULL(name)// Returns .T.
Servoy code example
varname=null;
globals.ISNULL(name); // returns true
Note: ISNULL() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ISUPPER() - globals.ISUPPER()
Determines whether the leftmost character of the specified character expression is an uppercase alphabetic character.
VFP code example
?ISUPPER('Abc')&& returns .F.
?ISUPPER('abc')&& returns .T.
?ISUPPER('9ab') && returns .F.
?ISUPPER('éb89')&& returns .T.
?ISUPPER('_bcdef')&& returns .F.
Servoy code example
cString = "Ábc";
cString.charAt(0).match(/[^W0-9_]/)!=null&&
cFirstCharacter == cFirstCharacter.toUpperCase();// returns true
// alternatively
globals.ISUPPER("Abc");// Returns true
globals.ISUPPER("abc"); // Returns false
globals.ISUPPER("9ab"); // Returns false
globals.ISUPPER("éb89"); // Returns false
globals.ISUPPER("_bcdef");// Returns false
Note: ISUPPER() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
JUSTDRIVE() - globals.JUSTDRIVE()
Returns the drive letter from a complete path.
VFP code example
?JUSTDRIVE(FULLPATH(CURDIR()))&& returns:C:
Servoy code example
var cPath =plugins.file.getHomeDirectory().getPath();
globals.JUSTDRIVE(cPath); // returns: C:
Note: JUSTDRIVE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
JUSTEXT() - globals.JUSTEXT()
Returns the characters of a file extension from a complete path.
VFP code example
?JUSTEXT("Document1.doc") && returns:doc
Servoy code example
globals.JUSTEXT("Document1.doc");// returns: doc
Note: JUSTEXT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
JUSTFNAME() - globals.JUSTFNAME()
Returns just the filename from a complete path.
VFP code example
?JUSTFNAME("c:\test\Document1.doc")&& returns:Document1.doc
Servoy code example
globals.JUSTFNAME("c:\\test\\Document1.doc");/ returns: Document1.doc
Note: JUSTFNAME() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
JUSTPATH() - globals.JUSTPATH()
Returns just the path from a complete path and filename.
VFP code example
?JUSTPATH("c:\test\Document1.doc")&& returns:c:\test\
Servoy code example
globals.JUSTPATH("c:\\test\\Document1.doc");/ returns: c:\test\
Note: JUSTPATH() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
JUSTSTEM() - globals.JUSTSTEM()
Returns the stem name (the file name before the extension) from a complete path and file name.
VFP code example
?JUSTSTEM("c:\test\Document1.doc")&& returns:Document1
Servoy code example
globals.JUSTSTEM("c:\\test\\Document1.doc");/ returns: Document1
Note: JUSTSTEM() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
LEFT() - utils.stringLeft
Returns a specified number of characters from a character expression, starting with the leftmost character.
VFP code example
myString = "Hello World"
MESSAGEBOX(LEFT(myString,6),64)
** result: Hello
Servoy code example
varmyString="Hello World"
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('',utils.stringLeft(myString,6))
// result: Hello
LEN() - string.length
Determines the number of characters in a character expression, indicating the length of the expression.
VFP code example
nLength1 =LEN("Hello World")&& count the number of characters (11)
nLength2 =LEN(ALLTRIM(customers.lastname))
Servoy code example
varcString="Hello World"
varnLength1=cString.length// count the number of characters
// gets the length of the customername from the
// customer field after trimming the spaces
varnLength2=utils.stringTrim(lastname).length
Note: LEN() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
LOCK() - databaseManager.acquireLock()
Attempts to lock one or more records in a table.
VFP code example
?LOCK() && lock the current record of the current table
?LOCK("customers") && lock the current record of the customers table
?LOCK("customers", "65") && lock record 65 of the customers table
?LOCK("customers", "1,2,3")&& lock records 1,2,3 of the customers table
Servoy code example
databaseManager.acquireLock(foundset, 0);// lock the current record
databaseManager.acquireLock(foundset, -1);
databaseManager.acquireLock(foundset, 65);// lock row 65
// Alternatively:
globals.LOCK(foundset, 0); // lock the current record
globals.LOCK(foundset, -1);// lock all rows
globals.LOCK(foundset, 65);// lock row 65
Note: LOCK() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
LOG() - Math.log()
Returns the natural logarithm (base e) of the specified numeric expression.
VFP code example
?LOG(3) && returns 1.09861228866811
Servoy code example
Math.log(3);// returns 1.09861228866811
// alternatively:
globals.LOG(3); // returns 1.09861228866811
Note: LOG() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
LOWER() - string.toLowerCase()
Returns the specified character expression in lowercase.
VFP code example
myString = "Hello World"
myString =LOWER(myString)
** result: hello world
Servoy code example
varmyString="Hello World";
myString=myString.toLowerCase();
// result: hello world
LTRIM() - globals.LTRIM()
Removes all leading spaces from the specified character expression. For ALLTRIM() the utils.stringTrim() alternative is available but for the LTRIM there is none.
VFP code example
?LTRIM("hello")&& returns:"hello"
Servoy code example
Code Reference - Messagebox()
The Messagebox function in VFP is well known and easy to use. The Servoy counterpart is not all that different and even more userfriendly and powerful. Nevertheless the MESSAGEBOX() function has been added to the VFP2Servoy Toolkit for your convenience.
It works the same as in VFP (except there is no timeout support) and it returns the button caption instead of a number wich I find more convenient. If you want it exactly the same it's a small change to make.
VFP code example
Syntax:
MESSAGEBOX(eMessagetext,[nDialogBoxType][,cTitleBarText][,nTimeout])
Sample 1
MESSAGEBOX("Hello World", 64)
Sample 2
MESSAGEBOX("Please try again", 48)
Sample 3
MESSAGEBOX("An error has occurred, the system will shut down now.",16)
Sample 4
IF MESSAGEBOX("Are you sure you want to exit the application?",36)=6
QUIT
ENDIF
Servoy code example
Syntax:
showInfoDialog(dialog_title, msg, [button1], [button2], [buttonN]);
Sample 1
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog("Servoy", "Hello World!");
Sample 2
plugins.dialogs.showWarningDialog("Servoy","Please try again");
Sample 3
plugins.dialogs.showErrorDialog("Servoy","An error has occurred, the system will shut down now");
Sample 4
var buttonChoice = plugins.dialogs.showQuestionDialog("Servoy","Are you sure you want to exit the application?","Yes", "No");
if (buttonChoice == "Yes")
{
application.exit();
}
Note: MESSAGEBOX() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
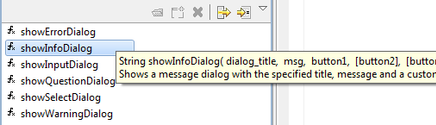
Summarizing
If you have trouble remembering the syntax then locate thepluginsnode in the Solution Explorer and expand it. Click on thedialogsnode and the List View window will show the available dialogs:
MAX() - globals.MAX()
Evaluates a set of expressions and returns the expression with the maximum value.
VFP code example
?MAX(23, 8, 79, 56) // Returns 79
?MAX("a", "z", "q") // Returns z
?MAX(DATE(2010,2,2),DATE(2011,1,1)// Returns Jan 1 2011
Servoy code example
globals.MAX(23, 8, 79, 56); // returns 79
globals.MAX("a","z","q"); // returns z
globals.MAX(newDate(2010,1,2),newDate(2011,0,1));// returns Jan 1 2011
Note: MAX()is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
MD | MKDIR - plugins.file.createFolder()
Creates a new directory or subdirectory on disk.
VFP code example
MD"c:\temp\sub1\sub2"&& create subfolder
Servoy code example
plugins.file.createFolder("c:\\temp\\sub1\\sub2");
// alternatively:
globals.MD("c:\\temp\\sub1\\sub2");
Note: MD() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
MIN() - globals.MIN()
Evaluates a set of expressions and returns the expression with the minimum value.
VFP code example
?MIN(23, 8, 79, 56) // Returns 8
?MIN("a", "z", "q") // Returns a
?MIN(DATE(2010,2,2),DATE(2011,1,1)// Returns Feb 2 2010
Servoy code example
globals.MIN(23, 8, 79, 56); // returns 8
globals.MIN("a","z","q"); // returns a
globals.MIN(newDate(2010,1,2),newDate(2011,0,1));// returns Feb 2 2010
Note: MIN() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
MINUTE() - date.getMinutes()
Returns the minute portion from a datetime expression.
VFP code example
?MINUTE(DATETIME()) // Returns a value between 0 and 59
Servoy code example
vard=newDate()
application.output(d.getMinutes())// Returns a value between 0 and 59
// OR using the MINUTE() function alternative:
vard=newDate()
application.output(globals.MINUTE(d)) // Returns a value between 0 and 59
Note: MINUTE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
MD | MKDIR - plugins.file.createFolder()
Creates a new directory or subdirectory on disk.
VFP code example
MKDIR"c:\temp\sub1\sub2"&& create subfolder
Servoy code example
plugins.file.createFolder("c:\\temp\\sub1\\sub2");
// alternatively:
globals.MKDIR("c:\\temp\\sub1\\sub2");
Note: MKDIR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
MOD() | % - %
Divides one numeric expression by another numeric expression and returns the remainder.
VFP code example
? 11 % 3 && returns 2
?MOD(11,3)&& returns 2
Servoy code example
11 % 3; // returns 2
// alternatively:
globals.MOD(11,3); // returns 2
Note: MOD() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
MONTH() - date.getMonth()
Returns the number of the month for a given Date or DateTime expression.
VFP code example
month =MONTH(DATE())&& 1=January, 2=February etc.
Servoy code example
vard=newDate();
varmonth=d.getMonth();// 0=January, 1=February etc.
Note: Alternatively use the MONTH() function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
msg() - plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog()
Simplified messagebox () function. When using plugins, dialogs, showInfoDialog(), or globals, MESSAGEBOX(), there are quite a lot of options you can fill in and code you need to type. If you just want to show a quick informative message with no other options, then this is the fastest way. By the way, this is not an existing VFP function, which is why it is not capitalized.
VFP code example
n/a
Servoy code example
AND, OR, NOT - &&, ||, !
Logical operators work with all data types and return a Logical value.
VFP code example
IFnAmount > 10 AND nAmount <= 100// logical AND
IFnAmount <= 10 OR (nAmount > 10 AND nAmount <= 20)// logical OR
IFNOT nAmount = 10// logical NOT (! and .NOT. are also valid)
Servoy code example
if(nAmount>10&&nAmount<=100)// logical AND
if(nAmount=10||(nAmount>10&&nAmount<=20))// logical OR
if(nAmount!=10)// logical NOT
NVL() - globals.NVL()
Returns a non-null value from two expressions.
VFP code example
eVar1 = .NULL.
eVar2 = 16
? NVL(eVar1, eVar2)&& Outputs 16
Servoy code example
vareVar1=null;
vareVar2=16;
application.output(globals.NVL(eVar1, eVar2))// Outputs 16
Note: NVL() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
AND, OR, NOT - &&, ||, !
Logical operators work with all data types and return a Logical value.
VFP code example
IFnAmount > 10 AND nAmount <= 100// logical AND
IFnAmount <= 10 OR (nAmount > 10 AND nAmount <= 20)// logical OR
IFNOT nAmount = 10// logical NOT (! and .NOT. are also valid)
Servoy code example
if(nAmount>10&&nAmount<=100)// logical AND
if(nAmount=10||(nAmount>10&&nAmount<=20))// logical OR
if(nAmount!=10)// logical NOT
OCCURS() - utils.stringPatternCount()
Returns the number of times a character expression occurs within another character expression.
VFP code example
?OCCURS("a", "abracadabra") && returns 5
Servoy code example
utils.stringPatternCount("abracadabra", "a");// returns 5
// alternatively:
globals.OCCURS("a", "abracadabra"); // returns 5
Note: OCCURS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
OS() - application.getOSName()
Returns the name and version number of the operating system under which the application is running.
VFP code example
?OS()&& returns Windows 6.01 under Windows 7 ;-)
Servoy code example
application.getOSName();
Note: OS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PADL() - globals.PADL()
Returns a string with the length of nLength padded with cPadChar on the left.
VFP code example
myVar = "9"
?PADL(myVar,2,"0")&& Outputs 09
Servoy code example
varmyVar="9";
application.output(globals.PADL(myVar,2,"0"))// Outputs 09
Note: PADL() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PADR() - globals.PADR()
Returns a string with the length of nLength padded with cPadChar on the right.
VFP code example
myVar = "23"
? PADR(myVar,5,"#") && Outputs 23###
Servoy code example
varmyVar="23";
application.output(globals.PADR(myVar,5,"#"))// Outputs 23###
Note: PADR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PARAMETERS() - arguments.length
Returns the number of parameters passed to the current function/method.
VFP code example
?PARAMETERS() && returns:number of parameters
Servoy code example
arguments.length
// Alternatively:
globals.PARAMETERS();// returns: number of parameters
Note: PARAMETERS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PCOUNT() - arguments.length
Returns the number of parameters passed to the current function/method.
VFP code example
?PCOUNT() && returns:number of parameters
Servoy code example
arguments.length
// Alternatively:
globals.PCOUNT();// returns: number of parameters
Note: PCOUNT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PI() - Math.PI
Returns the numeric constant pi.
VFP code example
? PI()
** result: 3.141592653589793 (depending on set decimals)
Servoy code example
Math.PI// PI is a constant and not a function as in VFP
// result: 3.141592653589793
^ | ** - Math.pow()
Returns base to the exponent power.
VFP code example
? 3 ^ 8 && Returns 6561
? 3 ** 8 && Returns 6561
Servoy code example
Math.pow(3,8); // returns 6561.0
// or alternatively:
globals.POWER(3, 8) // returns 6561.0
Note: POW() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PROPER() - utils.stringInitCap()
Returns from a character expression a string where each word is capitalized.
VFP code example
?PROPER("what's in a name?")&& returns: What's In A Name?
Servoy code example
utils.stringInitCap("what's in a name?");// What's In A Name?
// alternatively:
globals.PROPER("what's in a name?");// What's In A Name?
Note: PROPER() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
PUTFILE() - plugins.file.showFileSaveDialog()
Invokes the Save As dialog box and returns a JSFile object of the saved file.
Note: The PUTFILE() function returns a JSFile object from which you can retrieve all the file properties and methods. This is more powerful than just returning a string with the foldername and path.
VFP code example
cFileName =PUTFILE("File:", "test.txt", ".txt")&& invoke save as dialog
Servoy code example
// returns JSFile (see plugins.file.JSFile for list of props & functions)
varcFile= plugins.file.showFileSaveDialog("test.txt","Save file");
cFile.getPath();// c:\temp\test.txt
// alternatively:
// returns JSFile
var cFile=globals.PUTFILE("test.txt","Save file");
cFile.getPath(); // c:\temp\test.txt
Note: PUTFILE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
QUARTER() - globals.QUARTER()
Returns the quarter of the year in which a date(time) expression occurs.
VFP code example
?QUARTER(DATE()) // Returns 1,2,3 or 4
Servoy code example
vard=newDate()
Math.ceil((dDate.getMonth()+1)/3)// returns 1,2,3 or 4
// OR using the QUARTER() function alternative:
vard=newDate()
globals.QUARTER(d) // returns 1,2,3 or 4
Note: QUARTER()is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
QUIT - application.exit()
Ends execution of the current application. I don't think you would want to call globals.QUIT() instead of application.exit() but as a code reference it serves its purpose.
VFP code example
QUIT
Servoy code example
RAT() - string.lastIndexOf()
Returns the numeric position of the last (rightmost) occurrence of a character string within another character string. In Servoy the string starts at position 0!
VFP code example
?RAT("o", "Hello World")&& returns 8
Servoy code example
varcString="Hello World";
application.output(cString.lastIndexOf("o"))
// outputs 7 !!
Note: RAT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RAND() - Math.random()
Returns a random number between 0 and 1.
VFP code example
? RAND() // Returns a random value between 0 and 1
? RAND(100) // Use seed value to influence the generation
? RAND(-1) // Uses a seed value from the system clock
Servoy code example
Math.random(); // returns a random value between 0 and 1
globals.RAND(1,6); // roll the dice and generate a value of 1-6
Note: RAND() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
In Visual FoxPro a seed value parameter is available and the documenation states that the best random results wil be obtained by calling the RAND() function the first time with a negative argument the first time and subsequently without any argument. When searching for simular discussion around Javascripts Math.random() method I found a nice article that states that passing seed values is nonsense because they will be ignored by Javascript. However, it does warn about using the round function and urges you to use the Math.floor() function instead.
Although Visual FoxPro does not have min and max parameters that let you specify between which range you want to generate a random number I decided to improve the functionality of the RAND() function and add min and max parameters and use the code as described in this article. Special thanks to Regina Straminski for her excellent article.
RD - plugins.file.deleteFolder()
Removes a directory or folder from disk.
VFP code example
RD"c:\temp\" && remove the specified directory from disk
Servoy code example
plugins.file.deleteFolder("c:\\temp\\");// delete folder without warn.
plugins.file.deleteFolder("c:\\temp\\", true);// delete folder with warn.
// alternatively:
globals.RD("c:\\temp\\");
globals.RD("c:\\temp\\", true);
globals.RMDIR("c:\\temp\\");
globals.RMDIR("c:\\temp\\", true);
Note: RD() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RECCOUNT() - foundset.getSize()
Returns the number of records in the specified foundset.
VFP code example
?RECCOUNT()&& returns the number of records in the current table
?RECCOUNT("customers")&& returns the number of rows in customers table
Servoy code example
foundset.getSize();// returns the number of rows in the foundset !!
databaseManager.getFoundSetCount(foundset);// number of rows in the table
// Alternatively:
globals.RECCOUNT(foundset); // returns the number of rows
Note: RECCOUNT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RENAME - plugins.file.moveFile()
In VFP you can use the RENAME command to rename files within the same directory or move files to another directory.
Use the MOVEFILE() function to rename and move a file to another folder and the RENAME() function to just rename a file in the same folder.
NOTE: You cannot specify a file path in Servoy with single backslashes in it. The backslash is used to specify special characters (\t=tab for instance). You will have to remember to always use TWO backslashes instead of one to specify a single backslash (c:\\temp\\ instead of c:\temp\). We can't solve this in the function because "c:\temp" will arive in the parameter as "c: temp" (with a tab in it).
You cannot use wildcard characters in filenames in Servoy.
VFP code example
RENAMEc:\temp\test.xmlTOc:\temp\test.bak&& moves the file
Servoy code example
plugins.file.moveFile("c:\\temp\\test.xml","c:\\temp\\test.bak");
// alternatively:
globals.RENAME("c:\\temp\\test.xml", "c:\\temp\\test.bak");
Note: RENAME() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RENAME - plugins.file.moveFile()
In VFP you can use the RENAME command to rename files within the same directory or move files to another directory.
Use the MOVEFILE() function to rename and move a file to another folder and the RENAME() function to just rename a file in the same folder.
NOTE: You cannot specify a file path in Servoy with single backslashes in it. The backslash is used to specify special characters (\t=tab for instance). You will have to remember to always use TWO backslashes instead of one to specify a single backslash (c:\\temp\\ instead of c:\temp\). We can't solve this in the function because "c:\temp" will arive in the parameter as "c: temp" (with a tab in it).
You cannot use wildcard characters in filenames in Servoy.
VFP code example
RENAMEc:\temp\test.xmlTOc:\temp\test.bak&& moves the file
Servoy code example
plugins.file.moveFile("c:\\temp\\test.xml","c:\\temp\\test.bak");
// alternatively:
globals.RENAME("c:\\temp\\test.xml","c:\\temp\\test.bak");
Note: RENAME() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
REPLACE - globals.REPLACE()
Updates table records.
VFP code example
USEcustomers
m.city = customers.city
REPLACEcityWITH UPPER(m.city)
thisform.refresh()
Servoy code example
var_cCity = foundset.city;
foundset.city = _cCity;
REPLICATE() - globals.REPLICATE()
Returns a character string that contains a specified character expression repeated a specified number of times.
VFP code example
? REPLICATE("$",5)&& Outputs $$$$$
Servoy code example
application.output(globals.REPLICATE("$",5))// Outputs $$$$$
Note: REPLICATE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RLOCK() - databaseManager.acquireLock()
Attempts to lock one or more records in a table.
VFP code example
?RLOCK() && lock the current record of the current table
?RLOCK("customers") && lock the current record of the customers table
?RLOCK("customers", "65") && lock record 65 of the customers table
?RLOCK("customers", "1,2,3")&& lock records 1,2,3 of the customers table
Servoy code example
databaseManager.acquireLock(foundset, 0);// lock the current record
databaseManager.acquireLock(foundset, -1);
databaseManager.acquireLock(foundset, 65);// lock row 65
// Alternatively:
globals.RLOCK(foundset, 0); // lock the current record
globals.RLOCK(foundset, -1);// lock all rows
globals.RLOCK(foundset, 65);// lock row 65
Note: RLOCK() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
LEFT() - utils.stringRight
Returns the specified number of rightmost characters from a character string.
VFP code example
myString = "Hello World"
MESSAGEBOX(RIGHT(myString,5),64)
** result: World
Servoy code example
varmyString="Hello World";
plugins.dialogs.showInfoDialog('',utils.stringRight(myString,5));
// result: World
RMDIR - plugins.file.deleteFolder()
Removes a directory or folder from disk.
VFP code example
RMDIR"c:\temp\" && remove the specified directory from disk
Servoy code example
plugins.file.deleteFolder("c:\\temp\\");&& delete folder without warn.
plugins.file.deleteFolder("c:\\temp\\", true);&& delete folder with warn.
// alternatively:
globals.RD("c:\\temp\\");
globals.RD("c:\\temp\\", true);
globals.RMDIR("c:\\temp\\");
globals.RMDIR("c:\\temp\\", true);
Note: RMDIR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
ROUND() - Math.round()
Although both Servoy and Javascript have a round function they are not the same. The Math.round() function only rounds a number to an integer whereas Servoys utils.numberFormat() returns a numeric expression rounded to a specified number of decimal places, however it returns a localized string! The ROUND() function in the VFP2Servoy Toolkit was designed to mimic the ROUND() functionality as it has been implemented in VFP.
VFP code example
ROUND(23.463873,0)&& Returns 23
ROUND(23.463873,1)&& Returns 23.5
ROUND(23.463873,2)&& Returns 23.46
ROUND(23.463873,3)&& Returns 23.464
ROUND(23.463873,4)&& Returns 23.4639
ROUND(23.463873,5)&& Returns 23.46387
Servoy code example
Math.Round(23.463873, 2);// returns 23.46 as a string!
utils.numberFormat(23.463873, 2);// returns 23.46 as a string!
globals.ROUND(23.463873,0);// returns 23.0
globals.ROUND(23.463873,1);// returns 23.5
globals.ROUND(23.463873,2);// returns 23.46
globals.ROUND(23.463873,3);// returns 23.464
globals.ROUND(23.463873,4);// returns 23.4639
globals.ROUND(23.463873,5);// returns 23.46387
Note: ROUND() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RTRIM() - globals.RTRIM()
Removes all trailing spaces from the specified character expression. For ALLTRIM() the utils.stringTrim() alternative is available but for the RTRIM there is none.
VFP code example
?RTRIM("hello ")&& returns:"hello"
Servoy code example
globals.RTRIM("hello ");// returns: "hello"
Note: RTRIM() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
RUN - application.executeProgram() | application.executeProgramInBackGround()
Executes external programs.
VFP code example
RUNc:\windows\system32\calc.exe&& start windows calculator
RUN /Nc:\windows\system32\calc.exe&& start windows calculator NOWAIT
Servoy code example
varcResult=application.executeProgram("c:\\windows\\system32\\calc.exe");
application.executeProgramInBackground("c:\\windows\\system32\\calc.exe");
// alternatively:
varcResult=globals.RUN("c:\\windows\\system32\\calc.exe");
globals.RUN("c:\\windows\\system32\\calc.exe", true);
Note: RUN() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SCAN...ENDSCAN() - while()
Moves the record pointer through the currently selected table and executes a block of commands for each record that meets the specified conditions. This is where a lot of VFP programmers will have a hard time to let go of what they are used to: opening and selecting tables and modifying data very easily. As you may now know, Servoy has a one-table-per-form concept so approaching data is somewhat different. For large data manipulation operations you may want to send an update command directly to the database.
VFP code example
USEcustomers
SCAN
REPLACEcityWITH UPPER(city)
ENDSCAN
Servoy code example
vari = 1;
var_rec;
while(i <= foundset.getSize()) {// don't do this for > 1000 rows
_rec = foundset.getRecord(i);
_rec.city = _rec.city.toUpperCase();
i = i + 1;
}
SEC() - date.getSeconds()
Returns the seconds portion from a datetime expression.
VFP code example
?SEC(DATETIME()) // Returns a value between 0 and 59
Servoy code example
vard=newDate()
application.output(d.getSeconds())// Returns a value between 0 and 59
// OR using the SEC() function alternative:
vard=newDate()
application.output(globals.SEC(d)) // Returns a value between 0 and 59
Note: SEC() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SECONDS() - globals.SECONDS()
Returns the number of seconds that have elapsed since midnight.
VFP code example
?SECONDS() // number of seconds since midnight
Servoy code example
application.output(globals.SECONDS())// number of seconds since midnight
Note: SECONDS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SET MESSAGE TO - application.set StatusText
Set statusbar text and tooltip info.
VFP code example
SET STATUS BAR ON
SET MESSAGE TO"Record has been deleted"&& set status info
Servoy code example
application.setStatusText("Record deleted","Record has been deleted");
// alternatively:
globals.SET_MESSAGE_TO("Record deleted","Record has been deleted");
Note: SET_MESSAGE_TO() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SKIP - controller.setSelectedIndex(1);
Move the record pointer to the previous or next record.
VFP code example
// go to the next record
USECustomers
IF NOT EOF()
SKIP
ENDIF
// go to the previous record
IF NOT BOF()
SKIP-1
ENDIF
Servoy code example
// go to the next recordcontroller.setSelectedIndex(controller.getSelectedIndex()+1);
// go to the previous recordcontroller.setSelectedIndex(controller.getSelectedIndex()-1);
Note: SKIP() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SPACE() - globals.SPACE()
Returns a character string composed of a specified number of spaces.
VFP code example
?SPACE(3)&& returns:" "
Servoy code example
SQRT() - Math.sqrt()
Returns the square root of the specified numeric expression.
VFP code example
?SQRT(4) && returns 2
Servoy code example
Math.sqrt(4);// returns 2.0
// alternatively:
globals.SQRT(4); // returns 2.0
Note: SQRT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
STR() - utils.numberFormat()
Returns the character equivalent of a numeric expression.
VFP code example
?STR(17.456, 2)&& returns: 17.46 or 17,46 depending on locale
Servoy code example
utils.numberFormat(17.456, 2)//returns 17.46 or 17,46 depending on locale
utils.numberFormat(100006.749,'#,###.00');//returns 100,006.75
// alternatively:
globals.STR(17.456, 2);// returns: 17.46 or 17,46 depending on locale
Note: STR() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
STREXTRACT() - globals.STREXTRACT()
Retrieves a string between two delimiters.
VFP code example
** returns: important (case-sensitive)
?STREXTRACT("<B>This</B> text is <b>important</b>", "<b>", "</b>")
** returns: This (case-insensitive)
?STREXTRACT("<B>This</B> text is <b>important</b>", "<b>", "</b>", 1, 1)
** returns: important (2nd occurrence, case-insensitive)
?STREXTRACT("<B>This</B> text is <b>important</b>", "<b>", "</b>", 2, 1)
Servoy code example
varmyLine ="<B>This</B> text is <b>important</b>";
globals.STREXTRACT(myLine,"<b>","</b>"); // returns important
globals.STREXTRACT(myLine,"<b>","</b>", 1,true);// returns This
globals.STREXTRACT(myLine,"<b>","</b>", 2,true);// returns important
Note: STREXTRACT() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
STRTOFILE() - plugins.file.appendToTXTFile()
Writes the contents of a character string to a file.
VFP code example
STRTOFILE("Hello World!"+CHR(13), "c:\temp\hello.txt")&& appends string
Servoy code example
plugins.file.appendToTXTFile("c:\\temp\\hello.txt","Hello World!\n");
// alternatively:
globals.STRTOFILE("Hello World!\n","c:\\temp\\hello.txt");
Note: STRTOFILE() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
STRTRAN() - utils.stringReplace()
Searches a character expression for a second character expression and replaces each occurrence with a third character expression.
VFP code example
?STRTRAN("Hello World", "Hello", "Servoy")&& returns Servoy World
Servoy code example
varcString=utils.stringReplace("Hello World","Hello","Servoy");
application.output(cString);
// outputs Servoy World
NOTE! There is also a string.replace() function but if you use this the way you are used to it will only replace the first occurrence of the searchstring! This is because it expects a regular expression instead of a string as a first parameter!
We don't have regular expressions in Visual FoxPro but they are very powerful and you will benefit greatly if you learn how to use them!
Here's a quick tutorial on how to use regular expressions and here are some examples.
Note: STRTRAN() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
STUFF() - globals.STUFF()
Returns a character string created by replacing a specified number of characters in a character expression with another character expression.
VFP code example
?STUFF("Hello World", 7, 0, "there ") && returns: Hello there World
?STUFF("Hello there World", 7, 6, "in my ")&& returns: Hello in my World
?STUFF("Hello there World", 7, 6, "") && returns: Hello World
Servoy code example
globals.STUFF("Hello World", 7, 0, "there ");// returns: Hello there World
globals.STUFF("Hello World", 7, 6, "in my ");// returns: Hello there World
globals.STUFF("Hello World", 7, 6, ""); // returns: Hello World
Note: STUFF() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SUBSTR() - string.substr()
Returns a character string from the given character expression, starting at a specified position in the character expression and continuing for a specified number of characters. Watch out! The substring function is zero-based!
VFP code example
myString = "Servoy World 2011"
myString =SUBSTR(myString,8,5)&& Index starts at 1
** result: World
myString = "Hello World"
myString =SUBSTR(myString,1,1)&& Single character
** result: H
myString = "Hello World"
myString =SUBSTR(myString,7)
** result: World
NOTE! There is a string.substr(startPos, [length]) and a string.substring(startPos, [endPos]) function in Servoy. The difference is that the substr() function works like the SUBSTR() function in VFP and that the substring() functions second parameter is the endPosition as opposed to the length. See the examples for clarification.
Servoy code example
varstyle="color: #660066">varmyString="Servoy World 2011";
myString = myString.substr(7,5);// Index is zero-based!!
// result: World
varmyString="Servoy World 2011";
myString = myString.substring(7,12);// endpos instead of length
// result: World
varstyle="color: #660066">varmyString="Hello World";
myString = myString.CharAt(0);// This function does not exist in VFP
// result: H
varmyString="Hello World";
myString=myString.substring(6);
// result: World
NOTE! If you don't like the zero based substring implementation you can als use the following alternative as was pointed out to me by my good friend Alessandro Stefanoni:
// returns 'his'
varretval =utils.stringMiddle('this is a test',2,3);
SYS(0) - globals.SYS(0)
returns network machine information when using Visual FoxPro in a network environment. The same functionality is available by using ID().
VFP code example
?SYS(0) // returns machine id and user id
Servoy code example
application.getHostName() + " # "+security.getSystemUserName()
Note: SYS(0) is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SYS(2) - globals.SYS(2)
Returns the number of seconds that have elapsed since midnight.
VFP code example
?SYS(2) // number of seconds since midnight
Servoy code example
application.output(globals.SYS(2))// number of seconds since midnight
Note: SYS(2) is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SYS(3) - plugins.file.createTempFile()
Returns a legal file name that can be used to create temporary files. Servoys implementation is much more elegant than VFP's SYS(3) function. Keep in mind that VFP only generates a number that can be used as a temporary filename and that you have to add prefix and postfix such as temp_ and .tmp yourself. With the createTempFile function you can specify these as parameters and the users tempfile path is added as well.
VFP code example
?SYS(3) && Generates a legal file name to create a temporary file
Servoy code example
plugins.file.createTempFile("temp_",".txt");// generate tempfile name
// i.e.: C:\Users\MULTIT~1\AppData\Local\Temp\temp_2549553530386536937.txt
// alternatively:
globals.SYS(3);
Note: SYS() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
SYSMETRIC(1|2) - application.getScreenHeight() | application.getScreenWidth()
Returns the screenheight or width of the currently used display.
VFP code example
?SYSMETRIC(1) && returns the screenwidth
?SYSMETRIC(2) && returns the screenheight
Servoy code example
application.getScreenWidth();// returns the screenwidth
application.getScreenHeight();// returns the screenheight
// alternatively:
globals.SYSMETRIC(1);
globals.SYSMETRIC(2);
Note: SYSMETRIC() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
Thisform() - forms.frmFormName
Thisform returns an object reference to the current form in VFP. In Servoy this is slightly more complicated but not without reason. In VFP all properties and methods are publicly exposed and can be manipulated from outside the form. When adding PEMS you can make them private but the default properties are allways exposed.
In Servoy it's the other way around. By default a forms properties and method are private (not accessible from outside the form) unless they have been made public.
The form width for example is allways public in VFP and can be manipulated from outside the form. That's nice when you need it but not so nice when you don't want it. In Servoy the width property is only accesible from inside the form. However a getWidth() method has been added to allow readonly access to the property from outside the form. So if you want to make a property public create a method for it. This is comparable with VFP's access/assign options that you can set when creating custom PEMS.
Also note that Servoy forms have a controller through which a wealth of functions can be called which you would normally have to program yourself including all refresh logic which can be pretty tricky in VFP especially when you use multiple related grids which are used for data-entry and have validation rules which change data in them. In Servoy allmost all refresh logic is handled automatically. Try it!
VFP code example
?thisform.Name // Returns the name of the form
? frmCustomer.Name// reference to the form by objectname
?thisform.txtNameField // reference to a field inside a form
? frmCustomer.txtNameField // reference to a field outside a form
?_vfp.Forms.Item(1).myMethod() // form collection reference
Servoy code example
varfrm=currentcontroller.getName();// returns the name of the form
forms.frmCustomer; // returns the name of the form
elements.txtNameField; // reference to a field (in the form)
forms.frmCustomer.elements.txtNameField;// field reference outside form
forms[frm].myMethod(); // form collection reference
// reference to the subform in the active page of a tabpanel
vartab =forms.frmCustomer.elements.body_tab.tabIndex;
varformName =forms.frmCustomer.elements.body_tab.getTabFormNameAt(tab);
Note that many form-level control features are not available simply because Servoy takes care of them and you don't have to worry about it. Also note that a Servoy Form has a controller with a lot of methods for "controlling" your form. See the controller object node under each form in the Solution Explorer for a list of properties and methods.
Also note that in Servoy, forms can be combined together so that you may want to reference subforms individually as is shown in the code example above.
Third note is a warning not to try to create a thisform() function that works the same as in VFP or you'll generate a type-safety warning. Better is to reference the form explicitly. That way intellisense also works.
TIME() - date.toLocaleTimeString()
Returns the current system time in 24-hour, eight-character string (hh:mm:ss) format.
VFP code example
?TIME(DATETIME()) // Returns a value between 0 and 59
Servoy code example
vard=newDate()
application.output(d.toLocaleTimeString())// 17:37:43 CET
application.output(d.toTimeString()) // 17:37:43 GMT+0100 (CET)
// OR using the TIME() function alternative:
vard=newDate()
application.output(globals.TIME()) // 17:37:43
Note: TIME() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
TRANSFORM() - globals.TRANSFORM()
Returns a character string from an expression. In VFP the TRANSFORM() function also supports passing many formatcodes to format various types of data. In this (first) implementation only the conversion to a character string is supported.
VFP code example
?TRANSFORM(34.56)&& returns:"34.56"
?TRANSFORM(DATE())&& returns:"12-4-2011"
?TRANSFORM(.T.) && returns:".T."
?TRANSFORM(.NULL.)&& returns:".NULL."
Servoy code example
globals.TRANSFORM(34.56); // returns: "34.56"
globals.TRANSFORM(newDate());// returns: "12-4-2011"
globals.TRANSFORM(true); // returns: "true"
globals.TRANSFORM(null); // returns: "null"
Note: TRANSFORM() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
TYPE() - typeof()
Returns the data type of an expression. As you may know VFP advises the use of VARTYPE() instead of TYPE(). The difference is that with TYPE() the variable name must be surrounded by quotes and therefor be passed as a string literal. Internally the variable is then evaluated and the type returned. With the VARTYPE() function the variable itself is passed and the contents rather than the variable will be received as a parameter.
In Javascript the typeof() function is used to determine the type of an expression. However this would force us to use the feared eval() (which is nonsense if you know what your doing and don't eval user input). Besides that it is not possible to implement the TYPE() function in the same way as it is in VFP because the scope of the actual variable is unknown within the function.
Therefor the TYPE() and VARTYPE() function have both been implemented in the same way (the VARTYPE() way). The good news is that VARTYPE() also recognizes Date types which is not the case for Javascriptstypeof().
VFP code example
cText = "Hello"
?TYPE("cText")&& returns "C"
dDate =DATE()
?TYPE("dDate")&& returns "D"
** Possible types:
**
** C = Character, Memo, Varchar, Varchar (Binary)
** D = Date
** G = General
** L = Logical
** N = Numeric, Float, Double, Integer
** O = Object
** Q = Blob, Varbinary
** T = Datetime
** U = Undefined/unknown
** X = Null
** Y = Currency
Servoy code example
varcText = "Hello";
typeof(cText);// returns string
vardDate =newDate();
typeof(dDate);// returns object !
// Possible types: string, number, boolean, object, null, function,
// undefined
// alternatively:
varcText = "Hello";
globals.TYPE(cText);// returns string (NOTE! NO QUOTES)
vardDate =newDate();
globals.TYPE(dDate);// returns date !! (NOTE! NO QUOTES)
// alternatively:
varcText = "Hello";
globals.VARTYPE(cText);// returns string
vardDate =newDate();
globals.VARTYPE(dDate);// returns date !!
Note: VARTYPE() and TYPE() are functions of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
UPPER() - string.toUpperCase()
Returns the specified character expression in uppercase.
VFP code example
myString = "Hello World"
myString =UPPER(myString)
** result: HELLO WORLD
Servoy code example
varmyString="Hello World";
myString=myString.toUpperCase();
// result: HELLO WORLD
VAL() - utils.stringToNumber()
Returns a numeric value from a character expression composed of numbers.
VFP code example
?VAL("34.56")&& returns: 34.56
Servoy code example
utils.stringToNumber("34.56")// returns: 34.56
// but watch out!
utils.stringToNumber("-34.56")// returns: 34.56 too!!
// alternatively:
globals.VAL("34.56"); // returns: 34.56
Note: VAL() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
VARTYPE() - typeof()
Returns the data type of an expression. As you may know VFP advises the use of VARTYPE() instead of TYPE(). The difference is that with TYPE() the variable name must be surrounded by quotes and therefor be passed as a string literal. Internally the variable is then evaluated and the type returned. With the VARTYPE() function the variable itself is passed and the contents rather than the variable will be received as a parameter.
In Javascript the typeof() function is used to determine the type of an expression. However this would force us to use the feared eval() (which is nonsense if you know what your doing and don't eval user input). Besides that it is not possible to implement the TYPE() function in the same way as it is in VFP because the scope of the actual variable is unknown within the function.
Therefor the TYPE() and VARTYPE() function have both been implemented in the same way (the VARTYPE() way). The good news is that VARTYPE() also recognizes Date types which is not the case for Javascriptstypeof().
VFP code example
cText = "Hello"
?VARTYPE(cText)&& returns "C"
dDate =DATE()
?VARTYPE(dDate)&& returns "D"
** Possible types:
**
** C = Character, Memo, Varchar, Varchar (Binary)
** D = Date
** G = General
** L = Logical
** N = Numeric, Float, Double, Integer
** O = Object
** Q = Blob, Varbinary
** T = Datetime
** U = Undefined/unknown
** X = Null
** Y = Currency
Servoy code example
varcText = "Hello";
typeof(cText);// returns string
vardDate =newDate();
typeof(dDate);// returns object !
// Possible types: string, number, boolean, object, null, function,
// undefined
// alternatively:
varcText = "Hello";
globals.VARTYPE(cText);// returns string
vardDate =newDate();
globals.VARTYPE(dDate);// returns date !!
Note: VARTYPE() and TYPE() are functions of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
VERSION() - application.getVersion()
Returns the version information of VFP/Servoy.
VFP code example
?VERSION() && Visual FoxPro 09.00.0000.5815 for Windows
?VERSION(1) && Visual FoxPro date and serial number
?VERSION(2) && Version type (0=runtime, 1=standard ed. 2=prof.ed.
?VERSION(3) && Localized Visual FoxPro language
?VERSION(4) && Visual FoxPro version number in easily parsed format
?VERSION(5) && Visual FoxPro version number in format Mmm.
// test if running in developer edition
?VERSION(2)=2&& returns .T. when running developer edition
Servoy code example
application.getVersion(); // i.e.: 6.0.0 a6
// test if running in developer edition
application.isInDeveloper();
// alternatively:
globals.VERSION();
Note: VERSION() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit
WEEK() - globals.WEEK()
Returns a number representing the week of the year from a Date(time) expression.
VFP code example
?WEEK(DATE()) // Returns a value between 1 and 53
Servoy code example
vard=newDate()
application.output(globals.WEEK(newDate()) // ISO 8601 week nr
application.output(globals.WEEK(newDate(),1)// USA/Canada week nr
Note: WEEK() is a function of the VFP2Servoy Toolkit